- Home >
- About DM
About DM
認識糖尿病
-

Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder, primarily caused by prolonged elevated levels of sugar in the blood, leading to an excess of sugar beyond the kidney's capacity. Consequently, this excess sugar is excreted through urine, giving rise to the term "diabetes."
MORE -

Common Complications of Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic disease characterized by insufficient insulin secretion or ineffective use of insulin in the body. This leads to the accumulation of glucose in the bloodstream, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels. When the body is exposed to high blood sugar for an extended period, it is prone to various chronic complications. Depending on the affected organs, these complications can be categorized into the following sections:
MORE -
Diabetes and Chronic Wounds
The normal wound healing process involves four stages, including the hemostasis stage, inflammation stage, proliferation stage, and remodeling stage. In a typical wound healing scenario, after the hemostasis stage, the inflammation stage lasts for approximately 3 days, following which it transitions into the proliferation stage. The proliferation stage can last for 3-21 days, and subsequently, the wound enters the longer remodeling stage.
MORE -

Daily Care and Prevention of Diabetes
Diabetes is an invisible chronic killer, and with the aging population, as well as changes in dietary habits and lifestyle, the number of diabetic patients continues to increase. Diabetes is not just a symptom of high blood sugar; it can lead to many complications. Therefore, patients should not take it lightly. Starting with daily health care, maintaining the body's optimal condition at all times can slow down the progression of diabetes and prevent various complications.
MORE -

The Burden and Impact of Diabetes on Society
Diabetes has become a prevalent global disease, bringing about high medical costs that pose a considerable burden on both patients and society. Beyond the direct costs associated with diabetes, various complications and comorbidities contribute to significantly elevated healthcare expenses for patients. According to statistics from the National Health Insurance Administration under the Ministry of Health and Welfare in Taiwan, the healthcare cost for diabetic patients is 4.3 times higher than that for non-diabetic individuals. Moreover, medical costs increase with poor blood sugar control (HbA1C concentration), making it a substantial and noteworthy societal issue.
MORE -
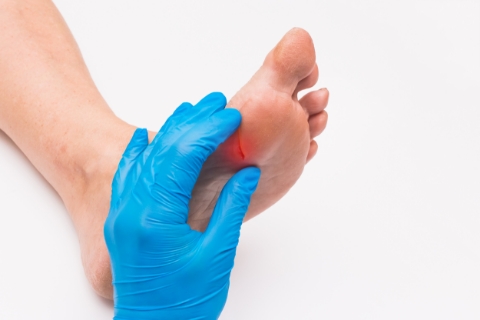
Diabetic Foot
Diabetes can give rise to one of its chronic complications known as "Diabetic Foot Ulcers" (DFU); according to statistics, approximately 1/4 of diabetic patients have faced the challenges of "Diabetic Foot" in their lives.
MORE -

Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
According to the Diabetes Care Foundation's newsletter "Diabetes Family" (2005), the treatment process for diabetic foot is extremely complex and requires collaboration across multiple disciplines within the healthcare team. This team may include foot care nurses, metabolism specialists, orthopedic surgeons, cardiovascular surgeons, plastic surgeons, rehabilitation specialists, and infectious disease healthcare professionals. Together, they assess the overall health of individuals with diabetes, the severity of wounds, peripheral vascular blockage, and infection status, among other factors. After integrating this information, a treatment plan is formulated.
MORE -

Daily Care of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Daily care for diabetic foot ulcers, in addition to following the general principles outlined below as treatment and daily guidelines for patients, should also pay attention to specific wound care considerations. The following will further elaborate on these points:
MORE
