Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcers

According to the Diabetes Care Foundation's newsletter "Diabetes Family" (2005), the treatment process for diabetic foot is extremely complex and requires collaboration across multiple disciplines within the healthcare team. This team may include foot care nurses, metabolism specialists, orthopedic surgeons, cardiovascular surgeons, plastic surgeons, rehabilitation specialists, and infectious disease healthcare professionals. Together, they assess the overall health of individuals with diabetes, the severity of wounds, peripheral vascular blockage, and infection status, among other factors. After integrating this information, a treatment plan is formulated.
According to the Diabetes Care Foundation's newsletter "Diabetes Family" (2005), the treatment process for diabetic foot is extremely complex and requires collaboration across multiple disciplines within the healthcare team. This team may include foot care nurses, metabolism specialists, orthopedic surgeons, cardiovascular surgeons, plastic surgeons, rehabilitation specialists, and infectious disease healthcare professionals. Together, they assess the overall health of individuals with diabetes, the severity of wounds, peripheral vascular blockage, and infection status, among other factors. After integrating this information, a treatment plan is formulated.
The commonly applied treatment plans in clinical practice
The commonly used treatment plans in clinical practice include non-invasive vascular testing (ABI, ankle-brachial index) or angiography to examine vascular lesions and blockages. In some cases, further procedures such as percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (Peripheral Arterial Angioplasty) or bypass angioplasty surgery for the lower limb arteries may be necessary to reconstruct peripheral vascular blockages and improve blood circulation.
common treatment plans and procedures In clinical practice
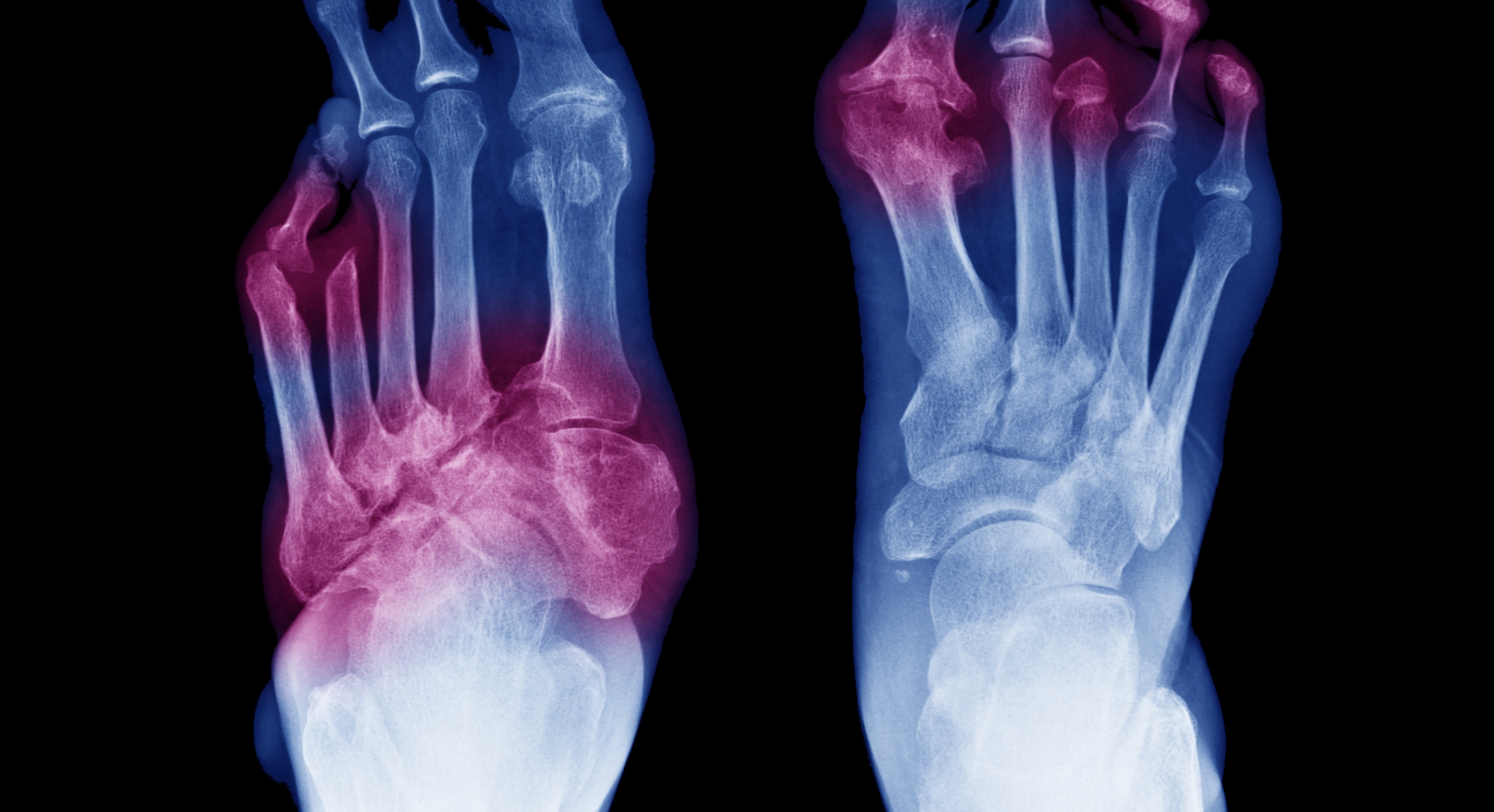
- Commonly, X-rays or probes are used to assess the severity of infection in the affected area.
- Surgical procedures, such as excision, drainage, and debridement, are performed by the surgical team to remove necrotic tissue and address local wound infections. Antibiotic treatment is administered based on the results of bacterial cultures.
- Maintaining good blood sugar control is crucial.
- Proper relief of pressure on the injured area is essential, including measures such as having the patient rest in bed, using supports to stabilize the affected limb, using crutches or a wheelchair for mobility, and wearing specially designed soft insoles or shoes with hard soles.
- High-pressure oxygen therapy can be employed to promote circulation and increase the chances of ulcer healing.
- After controlling the wound infection, skin graft surgery can be considered to enhance the chances of healing foot ulcers. Through multiple wound cleanings, local surgeries, and prolonged wound care, most diabetic patients have the opportunity to reduce the likelihood of high-level amputations.
In addition, for these complex assessments and treatment methods, Professor Chen Xigen from Tri-Service General Hospital proposed a simple mnemonic in 2021 for easy memorization:【V.I.P.D.F.】.
The meaning of the mnemonic also includes DF representing Diabetic Foot, meaning that every DFU patient is a VIP and must be properly
cared for.
- V
Refers to Vessel assessment, ensuring that the patient has no ischemic risk. Once vascular lesions are suspected, early diagnosis and intervention with percutaneous angioplasty, vascular reconstruction, or bypass surgery should be provided to prevent deterioration and affect wound healing.
- I
Refers to Infection Control. Effective infection control, including the treatment of osteomyelitis, is essential to prevent healing delay caused by infections.
- P
Refers to Pressure assessment. The pressure on the wound will lead to difficulty in wound bed cell migration, causing ischemia and necrosis, preventing effective tissue growth. Good offloading insoles or special diabetic foot offloading shoes can effectively prevent ulcers caused by inappropriate pressure on the feet.
- D
Refers to Debride, removing necrotic tissue on the wound, which can also affect wound healing. Effective wound debridement is needed to remove necrotic tissue that hinders healing, allowing the wound to grow smoothly. With the development of biotechnology, newly developed drugs offer new hope for rapid healing.
- F
Refers to Fast Healing. Fast healing can effectively reduce the risk of infection and subsequent amputation.
Through the V.I.P.D.F. mnemonic, diabetic foot patients can quickly and easily assess whether the wound can heal. Recent research indicates that the main reason for the poor healing of DFU wounds is chronic inflammation. Chronic inflammation results in the production of a large number of pro-inflammatory mediators in the wound cell environment, leading to a prolonged inflammatory state of the immune system, preventing wound granulation tissue proliferation and entering the healing stage. Therefore, research suggests that adjusting the inflammatory issues in the wound microenvironment can effectively help heal diabetic foot ulcers.
Poor healing of diabetic foot wounds leading to amputation is the main cause of disability in diabetic patients. Once amputated, it affects physical, psychological, life, work, or interpersonal relationships. Therefore, a comprehensive medical team needs to address the multiple issues in treating diabetic foot, ensuring patients achieve the best quality of life. The trend of increasing foot lesions in diabetes in recent years highlights the importance of prevention and disease education to avoid the occurrence of diabetic foot ulcers. Therefore, the care of diabetic feet requires joint efforts from healthcare professionals, patients, and their families.
(Photo credit: ShutterStock)
-
Reference:
- 黃兆山醫師。糖尿病足部潰瘍的評估與治療。出自糖尿病關懷基金會會訊糖尿病家族,2005
